10 Best Practices for Safely Shipping Lithium Ion Batteries
In recent years, the surge in electronic device usage has led to an increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries, necessitating a focus on the best practices for safely shipping lithium-ion batteries. According to a report by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), over 90 million lithium batteries were transported by air in 2022 alone, highlighting the critical need for stringent safety protocols. The potential hazards associated with shipping lithium-ion batteries, such as overheating, short-circuiting, and even combustion, underline the importance of adhering to established guidelines to ensure safe transit.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading figure in battery safety research, emphasizes that “the safe transport of lithium-ion batteries is not merely a regulatory obligation but a responsibility we must uphold to protect both people and the environment.” To mitigate risks, it is essential for shippers to adopt comprehensive practices, including proper packaging, labeling, and employee training. As the industry continues to evolve, following these best practices for shipping lithium-ion batteries will be paramount in safeguarding assets and promoting sustainable transport solutions.

Best Practices for Packaging Lithium Ion Batteries for Shipping
When it comes to safely packaging lithium-ion batteries for shipping, adhering to industry best practices is crucial. According to a report by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), improper handling of lithium-ion batteries has been linked to numerous incidents in the aerospace sector, leading to heightened regulations. Ensuring that batteries are packaged correctly not only mitigates risks but also complies with shipping laws. The best practices suggest using sturdy boxes designed to withstand transportation stresses, employing cushioning materials that absorb shock, and ensuring batteries are discharged to an appropriate state of charge before shipping.
Additionally, clear labeling and documentation of the shipment is essential. The United Nations recommends that packages containing lithium-ion batteries be marked with appropriate hazard symbols and warning labels. A comprehensive compliance guide by the U.S. Department of Transportation highlights that including documentation, such as the declaration of Dangerous Goods, can facilitate smoother transit and reduce delays. Furthermore, segregating batteries from other potential hazards and ensuring they are placed in a way that prevents movement during transit can significantly enhance safety. By following these guidelines, shippers can protect not only their packages but also the safety of transportation personnel and the public.
10 Best Practices for Safely Shipping Lithium Ion Batteries
| Best Practice |
Description |
Importance |
| Use Proper Packaging |
Utilize packaging that meets regulatory standards for lithium ion batteries. |
Ensures compliance and minimizes risk of damage during transit. |
| Label Packages Clearly |
Include appropriate hazard labels and warnings on packaging. |
Alerts handlers to the presence of hazardous materials. |
| Protect Battery Terminals |
Cover terminals to prevent short circuits during shipping. |
Reduces potential fire hazards caused by shorts. |
| Avoid Damaged Batteries |
Do not ship batteries that are cracked or damaged. |
Prevent potential leaks or explosions during transit. |
| Limit State of Charge |
Ship batteries at a charge level below 30%. |
Minimizes risk of thermal runaway incidents. |
| Select Experienced Carriers |
Choose shipping companies experienced in handling hazardous materials. |
Improves overall safety in the transportation process. |
| Follow Shipping Regulations |
Comply with international and local shipping regulations. |
Avoid legal penalties and ensure safe transport. |
| Educate Staff on Safety |
Train employees on proper handling and packaging of batteries. |
Enhances workplace safety and reduces accident rates. |
| Monitor Batteries During Transit |
Implement tracking systems to monitor condition en route. |
Allows for quick response to any incidents. |
Understanding Regulatory Compliance for Shipping Lithium Ion Batteries
When shipping lithium-ion batteries, understanding regulatory compliance is crucial to ensuring safety and legality throughout the transportation process. Various international and national regulations govern the shipment of these batteries due to their potential hazards, including fire risks and chemical leaks. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the United Nations (UN) provide guidelines that classify lithium-ion batteries based on their capacity and likelihood of causing incidents during transit. Compliance with these guidelines involves accurately labeling packages, adhering to packaging requirements, and completing necessary documentation.
Shipping companies must also stay informed about the specific regulations that apply to different modes of transport, such as air, sea, or road. For instance, air shipments are often subjected to stricter regulations compared to ground transportation, necessitating specialized training for personnel handling these shipments. Additionally, understanding the classification system used for lithium batteries is vital; they are typically categorized as Class 9 hazardous materials. This classification ensures that all potential hazards are accounted for during transportation and appropriate safety measures are implemented, helping to minimize risks and protect both the shipment and the personnel involved.
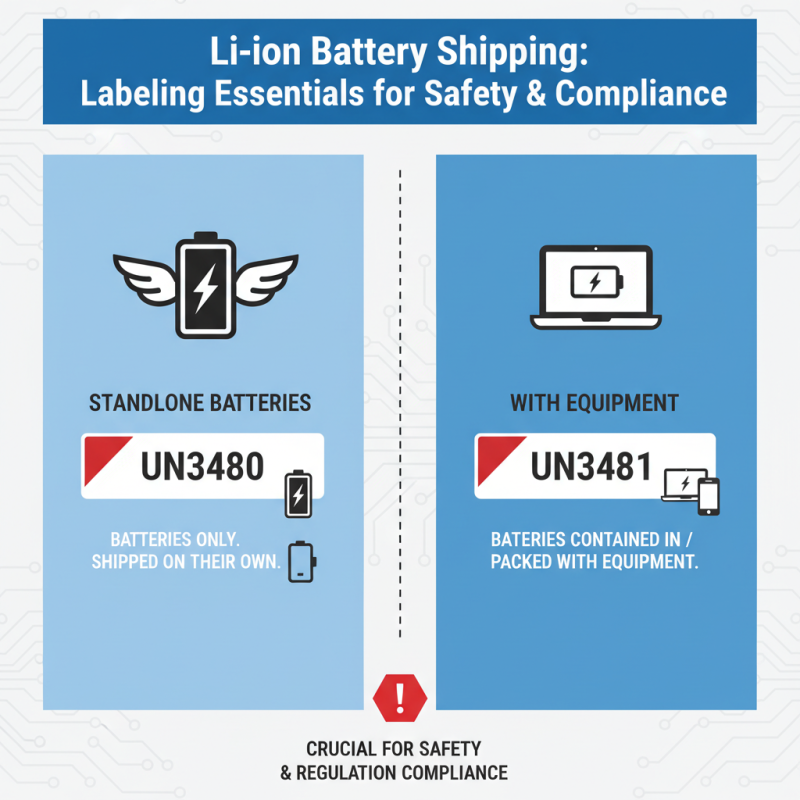
Essential Labeling Requirements for Lithium Ion Battery Shipments
When shipping lithium-ion batteries, adhering to strict labeling requirements is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with international regulations. The first essential label is the UN3480 or UN3481 marking, which identifies the type of shipment. UN3480 pertains to batteries that are shipped on their own, while UN3481 relates to those contained in or packed with equipment. Utilizing the correct UN number helps alert handlers and transporters to the specific risks associated with lithium-ion battery products.
Additionally, including a warning label that clearly indicates the shipment contains lithium-ion batteries is mandatory. This label should contain the appropriate symbols, including a depiction of a battery and accompanying safety warnings. A comprehensive hazard label not only informs workers about potential hazards but also assists in taking necessary safety precautions during handling. It is imperative that all labels are placed on the outer packaging and are clearly visible to ensure that the packages can be easily identified and handled safely throughout the entire shipping process.
Choosing Appropriate Shipping Methods for Lithium Ion Batteries
When shipping lithium-ion batteries, choosing the appropriate shipping methods is crucial to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. One recommended approach is to use carriers that specialize in transporting hazardous materials. These carriers are equipped to handle the specific requirements of lithium-ion batteries, which can pose fire hazards if not managed properly during transit. Additionally, it is essential to verify that the carrier follows relevant guidelines and has the necessary certifications to transport these types of batteries.
Moreover, the shipping method should involve packaging that meets industry standards for safety. Utilizing UN-approved packaging can significantly reduce the risks associated with transporting lithium-ion batteries. It is vital to ensure that the batteries are secured and cushioned to prevent movement within the packaging, which can lead to short circuits or physical damage. Furthermore, selecting ground shipping over air transport can mitigate risks, as ground methods generally have more stringent handling processes and reduce exposure to temperature fluctuations that can affect battery performance. By carefully considering these aspects, shippers can better ensure the safe transportation of lithium-ion batteries while adhering to best practices.
Handling and Storage Guidelines to Minimize Shipping Risks
Proper handling and storage of lithium-ion batteries are crucial to minimizing shipping risks. First and foremost, it's essential to store these batteries in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. High heat can lead to thermal runaway, causing the batteries to swell or even catch fire. Utilizing fire-resistant containers can further enhance safety during storage. Additionally, batteries should be kept in their original packaging or secured with adequate cushioning material to prevent movement during transit, which reduces the chance of short circuits.
Handling practices are equally important when preparing lithium-ion batteries for shipping. Workers should be trained to inspect batteries for any signs of damage or swelling before packing. Damaged batteries pose a significant risk and should be segregated for appropriate disposal. It’s also advisable to discharge the batteries to a safe level before shipment, as fully charged batteries are more prone to incidents. When packaging, ensure that terminals are insulated with non-conductive materials to prevent any accidental contact. Moreover, clearly labeling packages with appropriate hazard warnings will inform handlers of the contents and necessary precautions. Following these guidelines can significantly reduce potential hazards associated with shipping lithium-ion batteries.
10 Best Practices for Safely Shipping Lithium Ion Batteries
This bar chart illustrates the importance ratings of various best practices for safely shipping lithium-ion batteries. Each practice is assessed on a scale from 1 to 10, highlighting the critical aspects that contribute to minimizing shipping risks.