How to Choose the Right UN 3481 Battery for Safe Transportation
In the ever-evolving field of hazardous materials transportation, the UN 3481 battery category has emerged as a critical focus area for industries relying on lithium-ion technology. According to a report by the International Air Transport Association (IATA), incidents related to battery transport have increased significantly, underscoring the need for stringent safety measures during the shipping process. Hence, choosing the right UN 3481 battery is more pertinent than ever.
Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned expert in hazardous materials logistics, emphasizes the importance of proper selection and handling of these batteries: “The safety of transporting UN 3481 batteries hinges on understanding their specific characteristics and the regulations that govern them.” Her insights underline the necessity of rigorous adherence to safety standards to mitigate risks during transportation. With the growth of e-commerce and electronic devices, industry stakeholders must stay informed about best practices and regulations associated with UN 3481 batteries to ensure safe and compliant shipping methods.
With a landscape rapidly changing due to technological advancements and regulatory shifts, this guide aims to equip shippers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of UN 3481 battery transportation effectively. The right choice not only ensures compliance but also enhances safety for all parties involved.
Understanding UN 3481 Battery Regulations and Classifications
Understanding the regulations and classifications surrounding UN 3481 batteries is critical for ensuring their safe transportation. UN 3481 refers to lithium batteries contained in or packed with equipment, which are subject to stringent guidelines established by entities such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the United Nations. According to the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, these batteries must be declared and labeled appropriately, and a specific packaging method is required to prevent short circuits and protect the terminals. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to severe penalties and compromised safety during transport.
The classification of UN 3481 batteries largely hinges on their watt-hour capacity and cell arrangement. Released data from the Battery University states that batteries over 100 watt-hours per cell, under the UN 3480 classification, must follow different regulations compared to those below this threshold. For instance, cells or batteries under 300 watt-hours are generally permitted for air transport if packaged correctly. It is crucial for shippers to understand these distinctions and ensure compliance, as this not only aids in legal adherence but also reinforces safety when handling potentially hazardous materials. The proper categorization and adherence to packaging standards are paramount to reducing risks associated with lithium battery transportation.
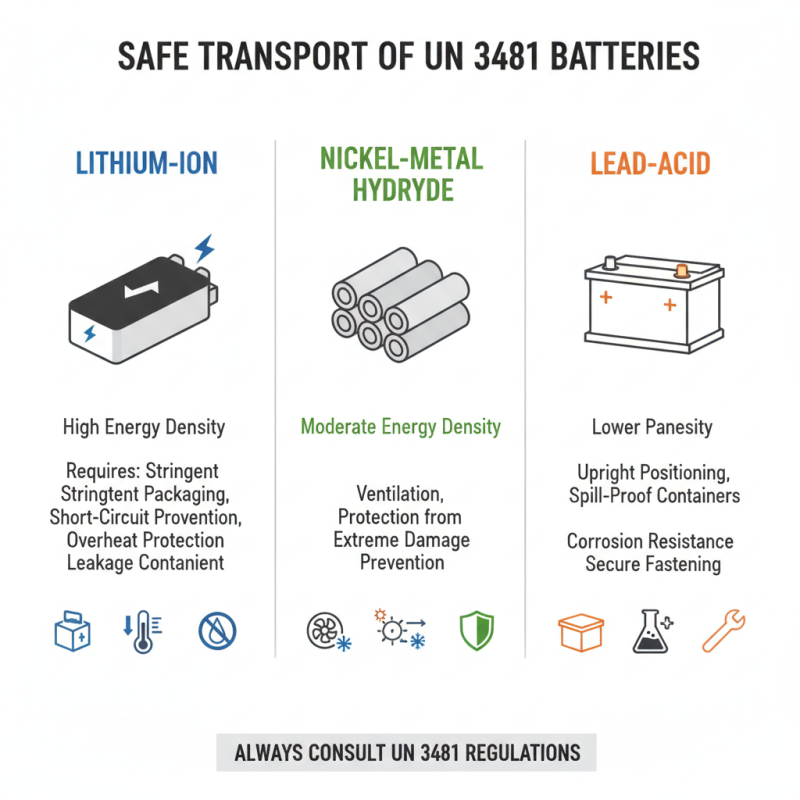
Evaluating Battery Types for Safe Transportation
When considering the transportation of UN 3481 batteries, it’s essential to evaluate the types of batteries available and their specific requirements for safe handling. There are various battery technologies, such as lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid, each with unique properties that influence their transportation safety. Lithium-ion batteries, for instance, are popular due to their high energy density but require stringent packaging and handling procedures to prevent short circuits, overheating, or leakage during transit. Understanding the chemistry and physical characteristics of the battery type will help determine the necessary precautions.
In addition to understanding battery types, one must also assess the packaging solutions tailored for each. UN 3481 batteries typically require packaging that meets strict safety regulations to minimize risks. This includes using robust outer containers, effective insulation materials, and appropriate cushioning to prevent movement during transit. Moreover, labeling and documentation are crucial in signaling the presence of batteries and ensuring compliant transport. Thoroughly evaluating these factors not only promotes safety but also fosters responsible logistics practices when transporting batteries.
Assessing Packaging Requirements for UN 3481 Batteries
When assessing packaging requirements for UN 3481 batteries, it is crucial to prioritize safety and compliance with relevant transport regulations. UN 3481 refers to lithium batteries packed with equipment or contained in equipment, and the characteristics of these batteries necessitate specific considerations during packaging. To begin with, the packaging must be capable of withstanding external pressure and potential impacts without compromising the integrity of the battery. This often involves utilizing strong, durable materials that can absorb shocks and prevent any leakage of the battery's contents.
Furthermore, proper labeling is a vital aspect of packaging for UN 3481 batteries. The outer packaging must display appropriate hazard symbols and handling instructions to ensure that all personnel involved in the transportation process recognize the potential risks. Additionally, utilizing inner packaging that provides adequate cushioning can significantly reduce the risk of damage. Properly designed inserts or foam padding can keep the batteries stable and protected from movement inside the box. In summary, meticulous attention to the packaging requirements for UN 3481 batteries not only safeguards the batteries themselves but also enhances the overall safety of the transportation process.
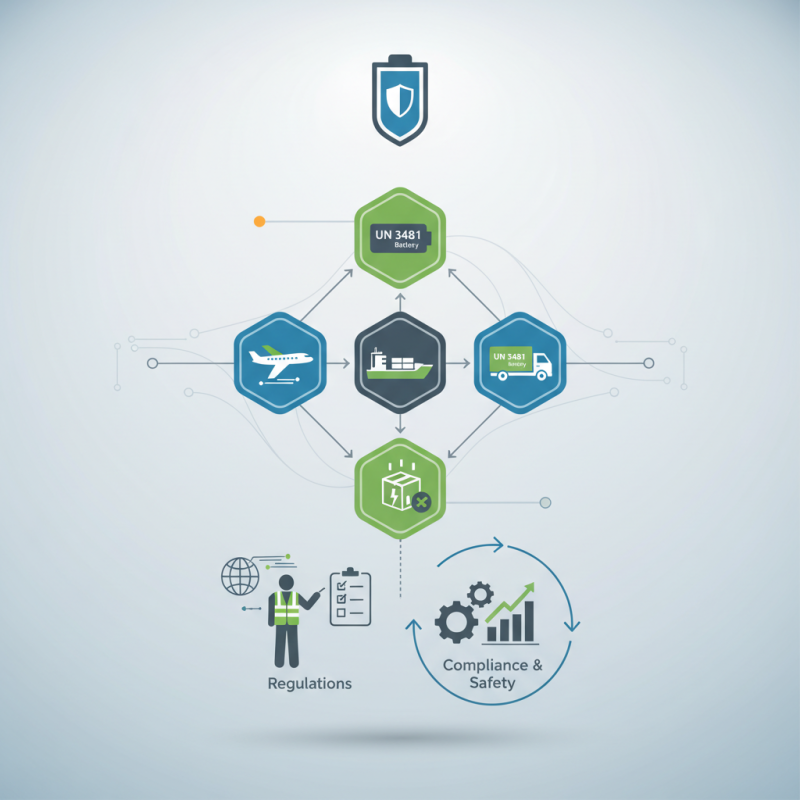
Identifying Transportation Modes and Their Safety Protocols
When transporting UN 3481 batteries, understanding the various transportation modes and the corresponding safety protocols is crucial to ensuring compliance and minimizing risks. Each mode—whether it be air, road, rail, or sea—has specific regulations established by authorities such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) or the Department of Transportation (DOT). For instance, air transport typically imposes stricter limitations on battery size and weight, along with rigorous packaging requirements, due to the heightened risks associated with altitude and potential incidents.
Road and rail transport, while generally more flexible, still require adherence to specified safety measures. This includes securing the batteries properly to prevent movement and damage during transit. Additionally, understanding the local regulations affecting the mode of transport chosen is essential, as different regions may impose their own sets of safety standards. In each case, using appropriate labeling and documentation will not only facilitate efficient transportation but also enhance safety by informing handlers of the potential hazards involved with the battery.
How to Choose the Right UN 3481 Battery for Safe Transportation - Identifying Transportation Modes and Their Safety Protocols
| Transportation Mode |
Safety Protocols |
Maximum Weight (kg) |
Packaging Requirements |
Additional Notes |
| Air Cargo |
Must notify carrier, label package, and follow IATA regulations. |
300 |
UN portable battery containers, inner packaging to prevent short circuits. |
Check airline policies for specific requirements. |
| Road Transportation |
Follow local regulations, ensure proper labeling. |
500 |
Pack in sturdy outer containers. Provide proper cushioning. |
Consider temperature exposure during transport. |
| Sea Freight |
Label properly and provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). |
1000 |
Use dry and waterproof outer packaging. |
Ensure good ventilation in the container. |
| Rail Transportation |
Follow domestic regulations, secure cargo properly. |
800 |
Utilize strap-down methods and appropriate pallets. |
Check for vibration and impact resistance requirements. |
Best Practices for Handling and Storing UN 3481 Batteries
When handling and storing UN 3481 batteries, adherence to best practices is crucial to ensure both safety and compliance with regulatory standards. UN 3481 refers to lithium-ion batteries packaged with equipment or contained in devices, and their specific handling protocols are outlined in the UN recommendations for the transport of dangerous goods. According to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the improper handling of lithium batteries can lead to serious incidents, with data indicating that nearly 24% of all air cargo incidents in the past five years have involved lithium battery shipments.
To minimize risks during storage, it’s essential to maintain optimal environmental conditions. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) recommends that lithium batteries be stored in cool, dry places, ideally between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F), away from flammable materials, to prevent thermal runaway. Additionally, ensuring that batteries are stored at a charge level between 30% and 50% can significantly reduce the risk of fire hazards during prolonged storage. Proper labeling and segregation from other types of hazardous materials are also vital; the batteries should be placed in dedicated storage areas with clear signage that meets the safety standards outlined by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Furthermore, handling protocols should include training personnel on the importance of visual inspections to identify any signs of damage or swelling in the batteries. The Lithium Battery Guideline (LBG) suggests conducting regular audits of storage areas and implementing a robust tracking system to monitor inventory levels and the condition of the batteries. By following these best practices, businesses can significantly reduce the risks associated with the transportation and storage of UN 3481 batteries, while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.