Essential Tips for Understanding Lithium Cells and Their Applications
Lithium cells are increasingly vital in today's technology-driven world. Their applications span from electric vehicles to portable electronics. Understanding the intricacies of lithium cells helps users appreciate their significance.
These cells offer high energy density and long cycle life. However, they also come with challenges. Safety concerns, such as overheating, require attention. Proper handling and storage methods are essential for users. Mismanagement can lead to risks, showing that awareness is key.
Moreover, as we advance, the demand for sustainable practices grows. Lithium cells play a critical role in renewable energy systems. Yet, we must consider their environmental impact. Recycling and responsible sourcing are hot topics in the industry. Recognizing these factors leads to more informed choices.
Understanding the Basics of Lithium Cells: Composition and Structure
Lithium cells are crucial in today's technology. They are found in many devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Understanding their composition is key to grasping how they work. These cells typically consist of a positive electrode, negative electrode, and electrolyte. The positive electrode often contains lithium cobalt oxide, while the negative one usually features graphite. This combination allows for efficient energy storage and delivery.
The structure of lithium cells affects their performance. Each cell comprises numerous layers, which enable efficient ion flow. However, this intricate design can also lead to issues. Overcharging or high temperatures can cause battery failure. This highlights the need for careful design and temperature management. There is also a potential risk of thermal runaway in poorly managed cells, emphasizing the importance of proper handling and technology in safety measures. Addressing such concerns is essential as we continue to rely on this technology in our daily lives.
Types of Lithium Cells: Variations and Their Specific Uses
Lithium cells come in several types, each designed for specific applications. The most common types are lithium-ion and lithium polymer cells. Lithium-ion cells are popular in consumer electronics. They provide high energy density and long cycle life. These cells power smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Their versatility makes them a preferred choice in many fields.
On the other hand, lithium polymer cells are lighter and more flexible. They use a gel-like electrolyte, enabling different shapes and sizes. This feature is crucial for drones and wearables, where weight matters. However, they usually have a shorter lifespan than lithium-ion cells. This poses a challenge for manufacturers. They need to find a balance between form factor and longevity.
Understanding the specific uses of these cells can be tricky. Applications may require different performance characteristics, including voltage and capacity. Some users may overlook this detail. It’s essential to recognize that not all lithium cells are interchangeable. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, and selecting the right one can make all the difference.
Applications of Lithium Cells in Modern Technology and Industries
Lithium cells are revolutionizing modern technology across various industries. Their lightweight nature and high energy density make them ideal for portable devices. For instance, smartphones and laptops rely heavily on lithium batteries for long-lasting performance. Consumers expect quick charging and extended use, which drives the demand for these cells.
In the automotive industry, lithium cells play a crucial role in electric vehicles. They not only power the cars but also enable regenerative braking. This system recovers energy that would otherwise be lost. Yet, some challenges remain. Issues like range anxiety and charging infrastructure still concern potential buyers. Also, the recycling process of these batteries is not yet perfected, leading to environmental debates.
Within the renewable energy sector, lithium batteries store energy for later use. Solar power systems often use them to balance supply and demand. This setup enhances efficiency. However, development is ongoing. Researchers need to address durability and cost-effectiveness. The journey to optimal lithium cell technology is still a work in progress.
Essential Tips for Understanding Lithium Cells and Their Applications
| Dimension |
Data |
| Cell Type |
Lithium-ion |
| Common Uses |
Electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops |
| Energy Density |
150-250 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life |
500-1500 cycles |
| Voltage Range |
3.0 - 4.2 V |
| Charging Time |
1-4 hours |
| Environmental Impact |
Recyclable, potential pollution if not disposed of properly |
| Future Trends |
Solid-state batteries, increased energy density, improved safety |
Safety Considerations and Risks Associated with Lithium Cell Use
Lithium cells are widely used in various applications, from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, their use comes with inherent risks that demand careful consideration. Overcharging or using defective lithium cells can lead to overheating. This might cause explosions or fires. Such incidents are not mere anecdotes; they have led to serious injuries and property damage in the past.
Knowing how to handle lithium cells is crucial. Always use compatible chargers. Store cells in a cool, dry place to avoid unnecessary heat. A simple oversight can turn dangerous quickly. Even a small dent or scratch on the cell's casing could compromise its integrity. If a cell feels hot to the touch, cease use immediately.
Awareness plays a significant role in safety. Regularly inspect your devices for any signs of damage. Understand warning signs like swelling or leaks. These are indicators that the cells may fail soon. Learning to recognize these issues can prevent accidents. The responsibility lies with users to remain vigilant when working with lithium technology.
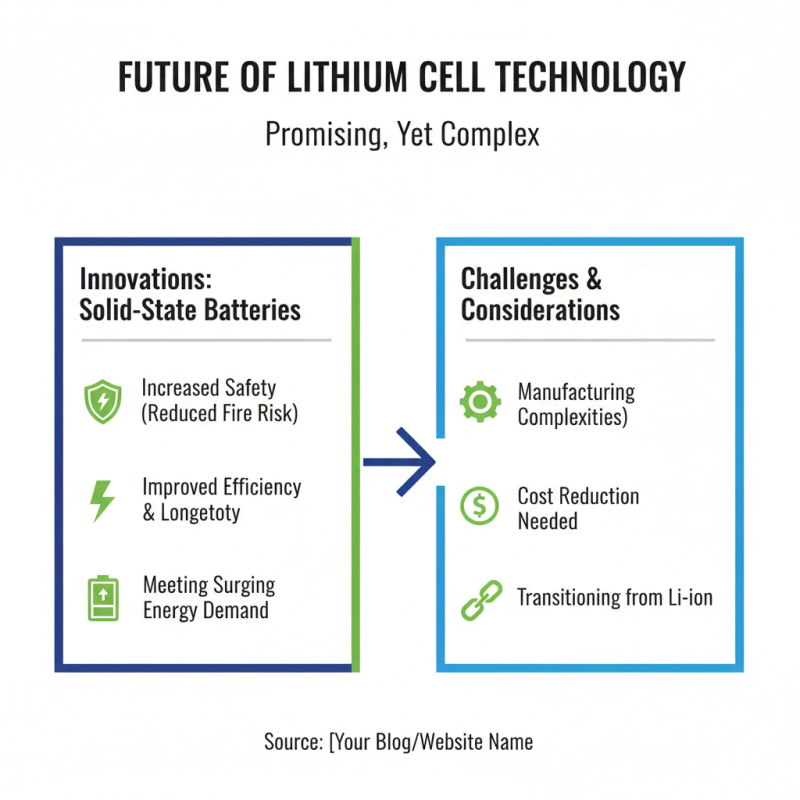
Future Trends and Innovations in Lithium Cell Technology and Applications
The future of lithium cell technology looks promising yet complex. As demand for energy storage surges, innovations are crucial. Researchers are exploring solid-state batteries, which offer increased safety and efficiency. These batteries could significantly reduce fire risks and improve longevity. However, the transition to solid-state technology isn't straightforward. Manufacturing challenges remain, and cost considerations must be addressed.
In addition, recycling lithium cells presents another pressing issue. As cell usage rises in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, waste management will become critical. Innovative recycling techniques are being developed, yet they face economic and technical hurdles. Efficient recycling processes could help recover valuable materials but require collaboration across industries. The journey toward sustainable lithium cell applications is fraught with challenges, reflecting the growing pains of an evolving technology.
Market trends show a shift towards circular economy models. This change is encouraging, but the pace is slow. Many companies are still hesitant to invest in these eco-friendly solutions. As society pushes for greener alternatives, the pressure mounts. Will innovators rise to the occasion and navigate these obstacles? Only time will tell.